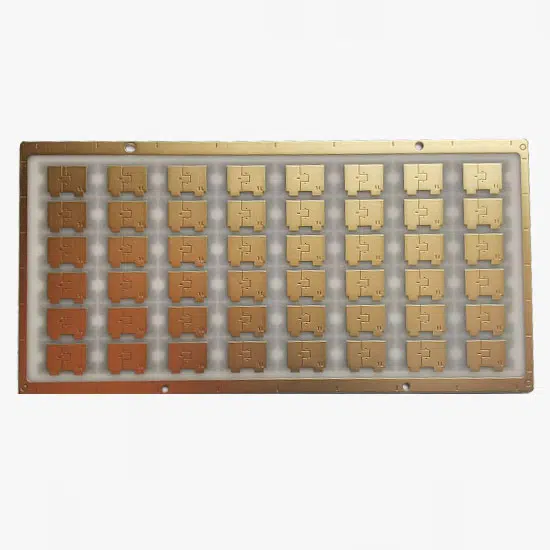
If you are looking for a PCB that is not made of traditional materials, then you should try a Ceramic PCB Board. This type of board is a good choice if you need to reduce costs, but is also better than traditional boards in some ways. This article will discuss the properties of this material and the advantages it offers. In addition to cost and properties, you can also learn more about its applications. In addition, you’ll discover how easy it is to use.
Ceramic PCB
Before deciding to buy a Ceramic PCB Board, consider the process for creating a prototype. A prototyping service is crucial to get a ceramic PCB in a timely manner. Do not chase the lowest quote; the ceramic PCB should be worth every dollar. A company should offer a large selection of shippers, and their facilities should be located near the fabric you intend to use. In addition, they should offer a rapid prototyping service.
Cost
A high-quality ceramic PCB board is a must for any project. These boards are used in chip-on-board modules, high-power circuits, and proximity sensors. Costs for a ceramic board vary depending on the size and finish required. While there are numerous advantages to using a ceramic PCB, it may be best for a small or mid-sized project. Read on to learn more. Here are some of the pros and cons of ceramic PCB board manufacturing.
Properties
A ceramic PCB board is a type of printed circuit board with good mechanical and thermal properties. This material is used for a variety of electronic applications because of its low thermal expansion and high operating temperatures. It is a great choice for high-power devices that are exposed to extremely high temperatures. This material can withstand high currents and is chemically and mechanically resistant, making it the ideal choice for use in a wide range of electronic applications.
Applications
There are several advantages of using Ceramic PCB Board in electronic systems. Due to its thermal properties, they are resistant to extreme temperatures and have excellent thermal conductivity. Unlike based PCBs, which are vulnerable to high temperatures and thermal conductivity changes, ceramic PCBs have similar thermal expansion coefficients to their base materials, making the board more efficient. In addition, thermal transfer of heat from a ceramic board is consistent across the entire PCB, ensuring that components run cooler.
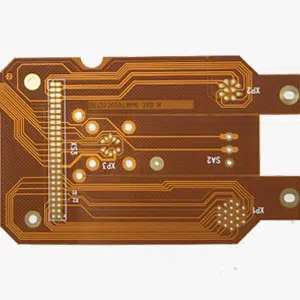
Manufacturing process
The manufacturing process of a ceramic PCB board is made using two different methods. One method is called the direct plate copper manufacturing, where the ceramic material is sintered without glass to produce a copper composite layer. After drying, the ceramic material is exposed to a trace pattern using a yellow light lithography process. After this step, the copper is electroplated and the photo-resist layer is removed. Another method is known as thick film ceramic manufacturing, in which the circuit layer is covered with a gold conductor paste and baked at over 1000 degrees to form a thin-film structure. However, due to high costs and high risk of contamination, this method is not popularly used in the production of PCBs.