What is the blockchain?
The blockchain is a system that creates digital, public ledgers. These ledgers are used to record transactions between parties over time. They can also store other information such as contracts and titles. The entries into this ledger cannot be changed or deleted once they are in the system. This helps to prevent fraud and tampering of records that has become so common in today’s society. I would like to see novel uses of crypto ledgers in our day-to-day lives. For example, we could have a ledger for a digital identity (similar to the blockchain behind Bitcoin). This would allow us to control and manage our digital identities on an immutable public system. The blocks are added to the blockchain chronologically and distributed across many different computers. This makes it almost impossible for hackers or anyone else to manipulate records on this system. The best way I can describe the blockchain is that it is like Google Docs but with some important differences:
Google Docs allows multiple people to work together on a document at any given time; however, those documents are hosted by Google’s servers. The docs are stored there until you delete them or move them somewhere else yourself (I know, I still don’t fully understand this). In comparison, when using a blockchain ledger like Bitcoin, there is no need for third party servers or hosting services because everyone maintains their own copy of the ledger automatically whenever they make changes—this means no one company controls your information! Instead of going through Google Docs like you would with traditional paper contracts/ledgers/bills/etc., with cryptocurrencies things get recorded onto one global public database that everyone has access to and can see at all times. This public ledger allows for transparency and trust between parties. The blockchain is sort of like a global spreadsheet that everyone has access to and can track changes to in real time. This means anyone can see what records have been added or changed through the system.
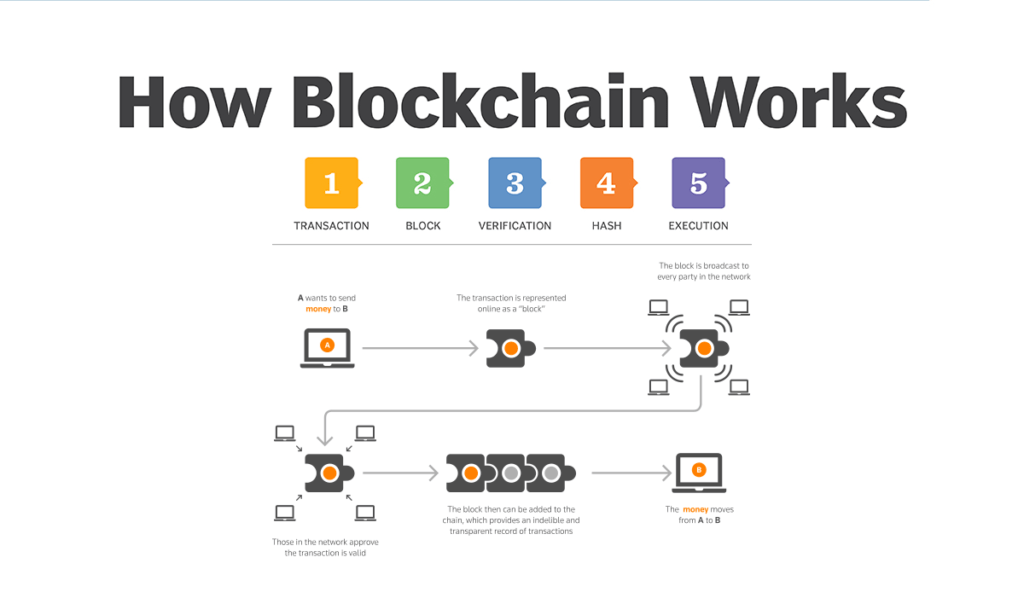
How does the blockchain work?
The way I understand it, every transaction ever made gets stored on one big digital ledger that is distributed across millions of computers around the world (this ledger is called the blockchain). For example, if I wanted to send money to someone else on a blockchain, we would both access this shared ledger (using our own copies) and make sure that we were both writing over the same entry in the list (“yourname” sent “x” amount of money to “myfriend’sname”). Once this transaction was made, entry after entry gets created until you get back to your original starting point (“you sent x amount of money” then “myfriend’sname received x amount of money”). Each new record includes information from its previous entries—allowing us all participants an accurate account of events as they happen in real time. These logs are added to the blockchain when they are validated by a node (a computer that is part of the network). This means that there has to be consensus between all nodes on the network before a new block can be added.
In order for transactions to be verified, they must meet certain criteria. For example, in Bitcoin each transaction must have inputs and outputs. An input is just like it sounds: something that was used as an input into another transaction (e.g., an old bitcoin address). The output of one transaction is used as an input for another transaction; this creates a chain reaction where you can trace back every single bit of currency ever used on the network—that’s pretty cool! Another way transactions are verified on these networks is through Proof-of-Work (PoW) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS). PoW is what most cryptocurrencies use today and it works like this: What happens in PoW? Nodes compete with each other to solve mathematical puzzles which then verify their entries into the blockchain ledger; however, you don’t want two people solving these at once because then both would have access to your information and could potentially steal it from you—so only one person gets rewarded with cryptocurrency after finishing their puzzle first.
The blockchain is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to change how we interact with each other and with governments. I am extremely excited about its potential uses, and I hope to see more novel uses of crypto ledgers in our day-to-day lives. That’s all for now!