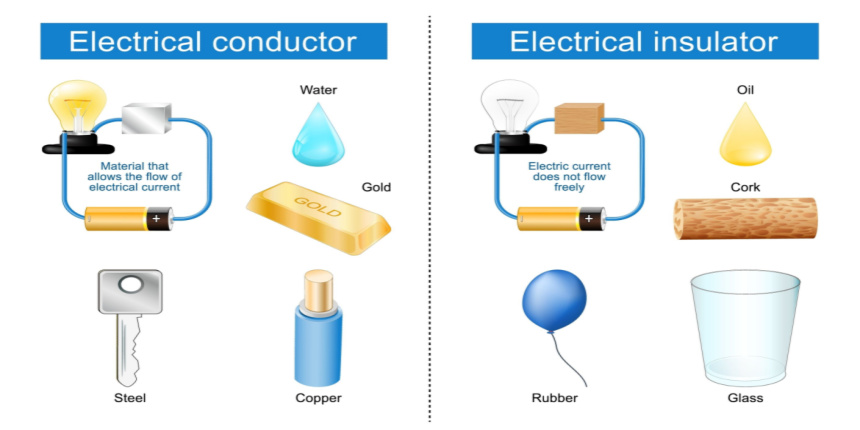
Certain substances have the ability to allow electricity to pass through them with ease, and these substances are referred to as electrical conductors. A large number of metals like copper, iron, and steel are highly efficient electrical conductors. Hence, electrical components that require the passage of electricity are generally constructed using metal.
For instance, metal is utilised in plugs to facilitate the transfer of electricity from a wall socket, through the plug and into devices like televisions or radios. In a light bulb, the metal filament conducts electricity and illuminates the bulb. Materials that impede the flow of electricity through them are called electrical insulators. Materials like plastic, wood, glass, and rubber are deemed to be good electrical insulators. For this reason, they are utilised to cover objects that conduct electricity. The plastic covering surrounding wires is an electrical insulator, and it prevents individuals from experiencing electric shock.
Let’s get technical:
Most metals exhibit a propensity to conduct electrical current due to their low resistance. The process by which electrical current flows through a wire is termed as conduction, and substances that facilitate this are referred to as conductors. Most metallic elements have a natural inclination to allow the flow of electrical current because they possess a property of low resistance. The process by which an electric current travels through a conductor is referred to as conduction. Conductors are substances that enable this process. Let’s define a conductor. Understanding the metal structure helps in comprehending why metals conduct electricity efficiently. Electrons usually orbit around the nucleus of atoms and cannot escape due to the strong electrostatic forces of attraction between negatively charged electrons and positively charged nuclei. The electrons remain bound to the nucleus. In metals, the outer electrons orbit farther from the nucleus, which results in weaker forces binding them. This weak force on the outer electrons enables them to move comparatively freely from one atom to another in metals. These electrons are known as free electrons or delocalized electrons. Materials containing numerous free electrons, such as metals, are considered to be excellent electrical conductors since these free electrons can move through the metal when a potential difference is applied.
Copper or silver, metals with a higher number of free electrons, are the best conductors as they have the lowest resistance. In contrast, metals with fewer free electrons, such as tin or lead, display a higher level of resistance and are hence not as efficient conductors. Metals consist of neatly arranged positive ions that represent atoms without their outer electrons. The arrangement is referred to as a crystal lattice with a sea of free electrons that can move among the ions Understanding the structure of metal helps explain why metals are efficient electrical conductors. Electrons typically revolve around an atom’s nucleus and cannot escape due to the strong electrostatic forces between negatively charged electrons and positively charged nuclei. These forces keep the electrons bound to the nucleus. In metals, the outer electrons orbit farther from the nucleus, resulting in weaker forces that bind them. The weak force allows outer electrons to move relatively freely from one atom to another in metals. Such electrons are known as free or delocalized electrons. Materials containing many such electrons, such as metals, are regarded as excellent electrical conductors because they can move through the metal when a potential difference is applied. Copper or silver, which have a higher number of free electrons, are the best conductors because they have low resistance. Conversely, materials with fewer free electrons, such as tin or lead, display greater resistance and are less effective conductors. Metals consist of positively charged ions arranged in a crystalline structure, representing atoms without their outer electrons. The pattern is called a crystal lattice with a large number of free electrons that can move among the ions.
A bit more on Insulators:
Substances like plastic, rubber, and glass, which are non-metals, have a high level of resistance, and hence they prevent or limit the smooth flow of electric current. These materials are known as insulators because they do not allow the easy movement of electric charges. Non-metals possess a low proportion of electrons that are free, making them poor electrical conductors and hard for electricity to flow through. Electrical lines are frequently encased with insulation materials, like plastic or rubber, to protect people from electric shocks. Plastic insulation helps to prevent direct contact with the metal wire within mains electrical cables, which could cause dangerous electric shocks. The plug casing is usually made of plastic or rubber to provide additional insulation. Graphite, a non-metal, is an exception to the rule, as it is an excellent electrical conductor. Graphite is used in the core of most pencils, and it can be sharpened at both ends and used in place of a wire to complete an electrical circuit.
How about liquids?
Substances like oil, alcohol, and distilled water exhibit poor electrical conductivity and are categorised as insulators. But electrolytes, like rainwater, tap water, and salt water, can conduct electricity and have dissolved minerals and salts in them. Gases generally do not conduct electricity efficiently, which is why electric currents cannot flow through the air easily. A lightning strike or an electric spark jumping across a distance are two instances in which electrical currents can travel through the air. To learn more about electrostatics and electrical shocks, delve deeper into the subject matter.
In Conclusion
To summarise, electrical conductors are substances that facilitate the easy flow of electrical current, while insulators impede the flow of electrical current. Metals, especially those with numerous free electrons, are excellent conductors of electricity. Non-metals, otherwise, tend to have high resistance and do not conduct electricity well, making them good insulators. Liquids like oil, alcohol, and distilled water are poor electrical conductors, while electrolytes like tap water and salt water can conduct electricity. Gases like air do not typically conduct electricity very effectively, but in certain circumstances, electrical currents can pass through them.